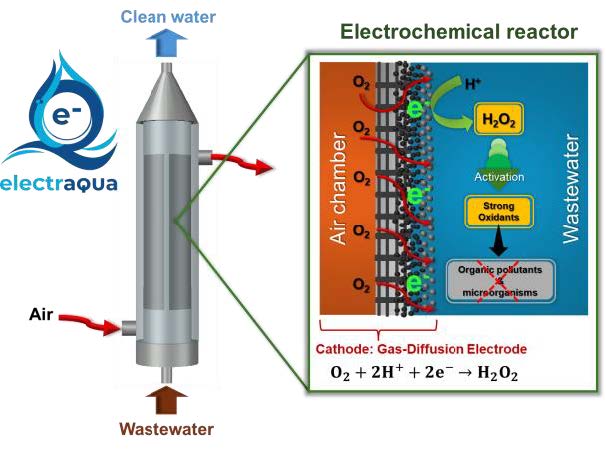
Water-processing electrochemical reactor
Advantages
- Produce-and-Use concept: In-situ generation of the main reagents needed (e-H2O2 and Fe2+ regeneration), no storage.
- Complete degradation of persistent organic pollutants and microorganisms.
- Larger volumetric capacities as compared to conventional electrochemical reactors.
- Low energy consumption and possibility to treat poorly conductive water.
Goal
Find early-stage investors to undertake pilot tests for technology validation in production sites (TRL 6-7) and further commercialization through plant manufacturing and licensing agreements.
Patent
International Patent Application No. PCT/EP2021/053501.
Priority date: 13 February 2020. Now in National stages (EU, USA, China).
Reference
UBTT0359
Contact
Dr. Sancho Moro
Email: smoro@fbg.ub.edu
Tel: +34 673388625
Water-processing electrochemical reactor
Executive summary
Researchers from the University of Barcelona (UB, Spain) have engineered a new electrochemical reactor for in-situ production of hydrogen peroxide (e-H2O2) and its immediate activation for advanced water treatment (i.e., so-called quaternary treatment). The new system can be combined with commercial pre-/post-treatments, ensuring a high removal of organic micropollutants and microorganisms in different industrial sectors (not limited to):
- Pharma industry, Cosmetics & Fine chemicals;
- Agrifood (pesticides);
- Food & beverage;
- Tertiary/quaternary urban wastewater.
Introduction
Clean water scarcity combined to increasing water pollution caused by human activities poses global challenges, being difficult to ensure universal, equitable and sustainable development. Under this scenario, greener and more efficient strategies are demanded to guarantee full access to safe water. In particular, the removal of organic micropollutants and microorganisms from wastewater becomes a main target, as anticipated by new water regulations drafted worldwide.
Description
The core of the wastewater treatment system is an innovative electrochemical reactor with tubular design, intended for the electrochemical production of H2O2 and its immediate activation to produce strong oxidants, thereby allowing an efficient decontamination and disinfection in continuous-flow mode (KPIs found at 1-5 l/h). Worth noting, air, electricity and a trace amount of catalyst are the main consumables, avoiding costly or dangerous chemicals. Moreover, the pioneering design of the electrochemical reactor increases the treatment capacity and reduces the energy consumption. The electrochemical system can be easily connected to existing treatment units to enhance their effectiveness. The dependence on supply chains and hazardous chemicals is importantly reduced.
This technology is intended to be used as an advanced treatment, meaning that is suitable for conditioning the effluents before discharge or even for wastewater regeneration. Hence, the system can be employed to treat a wide range of wastewater, but it is especially relevant to degrade pharmaceutical residues.
Current stage of development
- Proof of concept (TRL 5, 10-100 l/h) at laboratory scale, demonstrating the robustness for e-H2O2 production in continuous-flow operation mode.
- Currently validating the KPIs in a relevant environment (urban wastewater and actual wastewater provided by pharmaceutical companies that act as stakeholders).
- Brand new spin-off company (ELECTRAQUA TECH S.L.) created in November 2024.

