New anticancer agents for photodynamic therapy
New anticancer agents for photodynamic therapy
The challenge
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a technique commonly used to treat different types of cancers, especially skin cancers, and other diseases associated to the skin. This technique is based on the administration of a photosensitizer agent (PS) that, in the presence of oxygen and when exposed to light of the appropriate wavelength, is excited and produces highly cytotoxic reactive oxygen species (ROS) that destroy cancer cells.
Currently, the most widely used PSs are based on organic fluorophores, which exhibit several drawbacks, including a lack of activity under hypoxic conditions and auto-degradation due to photobleaching. With the aim of developing an optimal PS for combating cancer more efficiently with PDT, researchers from the University of Barcelona are currently working on the development of novel PSs with operability within the phototherapeutic window (650-800nm) and under hypoxic conditions with the aim of treating deep-seated hypoxic tumors.
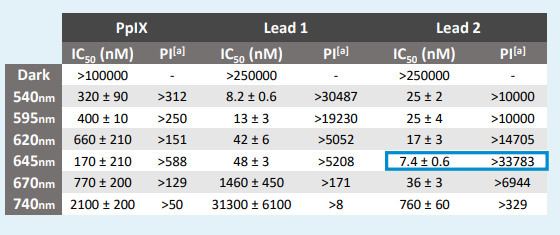
Technology
The researchers have developed a new family of PSs that can be efficiently photoactivated with far-red and NIR light. This radiation is non-toxic and penetrates deeper into human tissues than blue or green light. In addition, the PSs are highly photostable, cell permeable and have a clear subcellular target (mitochondria), which makes them promising candidates for clinical use. So far, several PS candidates have been synthesized and biologically evaluated in a panel of cancer cell lines under visible and NIR light. It is important to note that the compounds remain highly phototoxic under hypoxia conditions, which would allow to expand the potential applications of PDT for treating deep-seated hypoxic tumors. In addition, the PSs developed so far can be functionalized with other accessory molecules such as targeting ligands to deliver them selectively to cancer cells or even with other antitumoral agents that could be photoreleased when the PSs are exposed to light.

